ELECTIVE . SYSTEM DESIGN . WASTE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
My Roles and Responsibilities
In this elective, I was responsible for understanding the existing system design through primary research (Research methodology), secondary research, and field visits to better understand our stakeholders and come up with system design solution.
About Project
Personal Project ( college elective)
Semester 7 (8+ weeks )
Team: 6 classmates
Project Brief
The aim of this project is to implement a sustainable system design within the leather shoe industry by focusing on bridging the gap between the problem and the existing system in a manageable way. The core objective of the project is to identify the underpinning opportunities and challenges involved in creating recycling solutions for leather shoe waste.
Tools
Problem Background
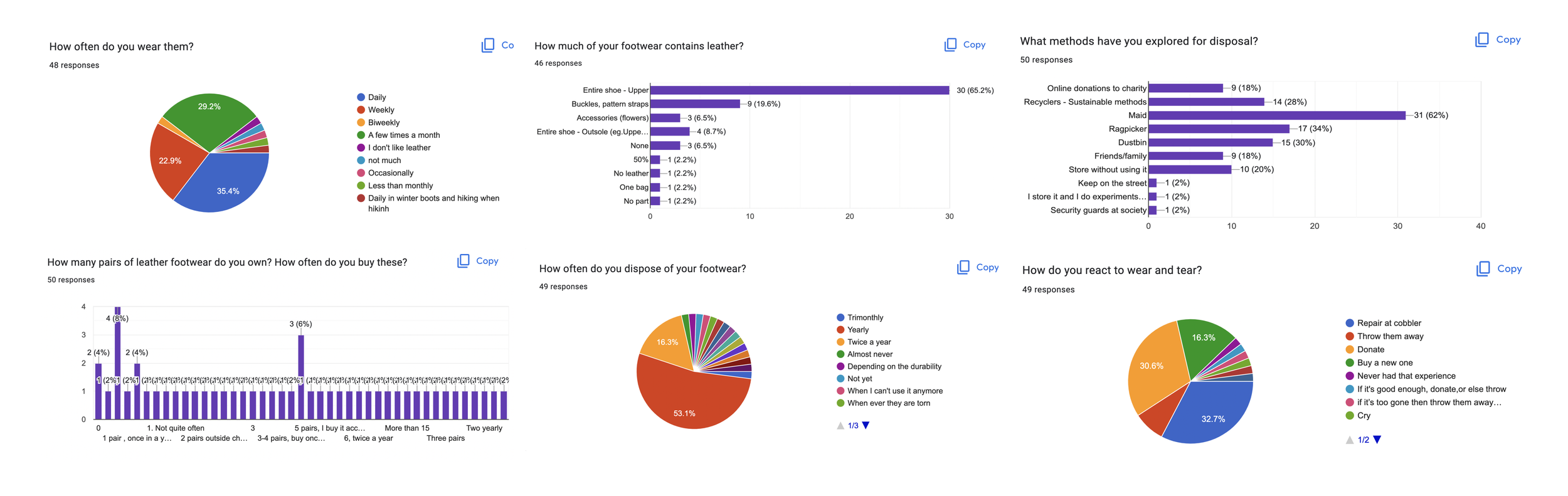
Consumer Behavior On Leather waste
53.1%
Dispose their footwear every year
62%
pass their old footwear off to the to someone else(maid)
65.2%
Claim the upper portion of their shoes is made of leather
full report here
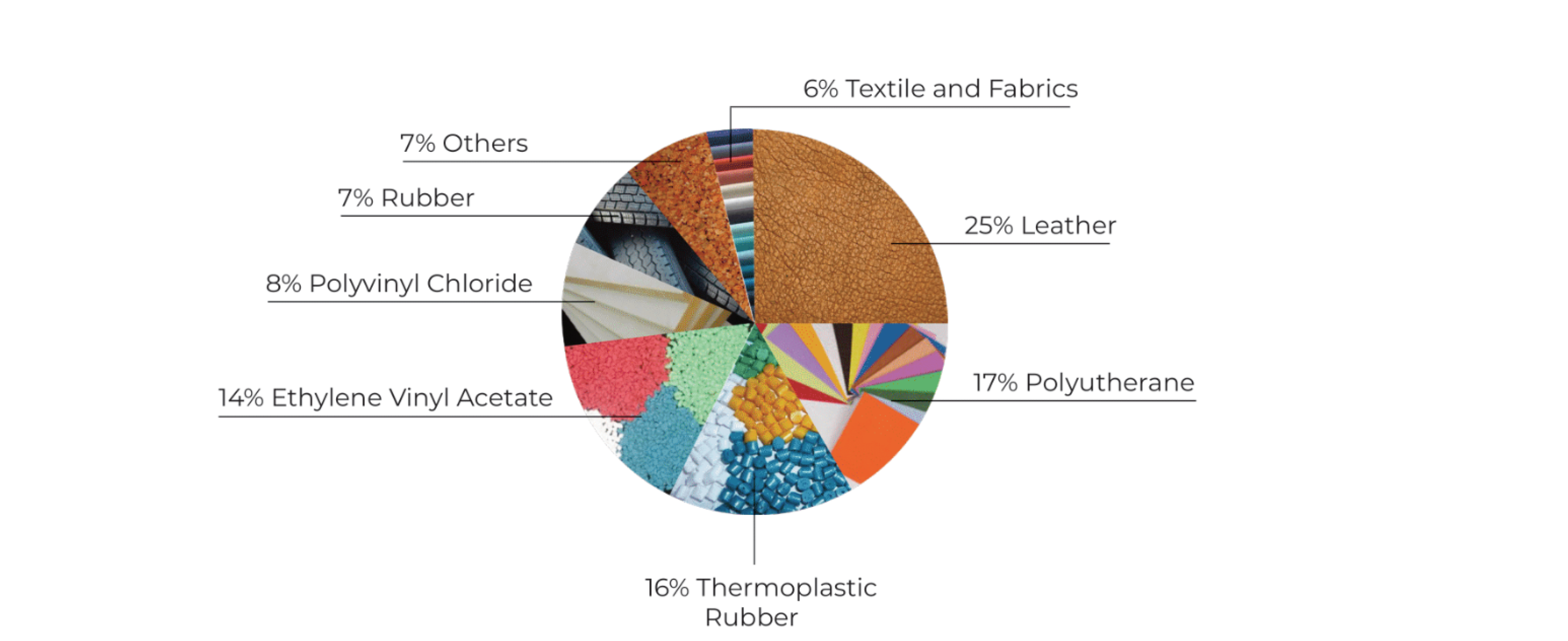
The footwear industry is a manufacturing sector that utilizes a wide variety of materials and processes to produce a range of distinctly different products, from sandals to specialized safety footwear. Shoes are designed to fulfill various consumer requirements relating to function and fashion and incorporate various designs and styles. In addition, a range of distinctly different materials such as leather, synthetic materials, rubber, and textile are commonly used in shoe manufacturing
Material Composition of an average shoe
Footwear Industry in India
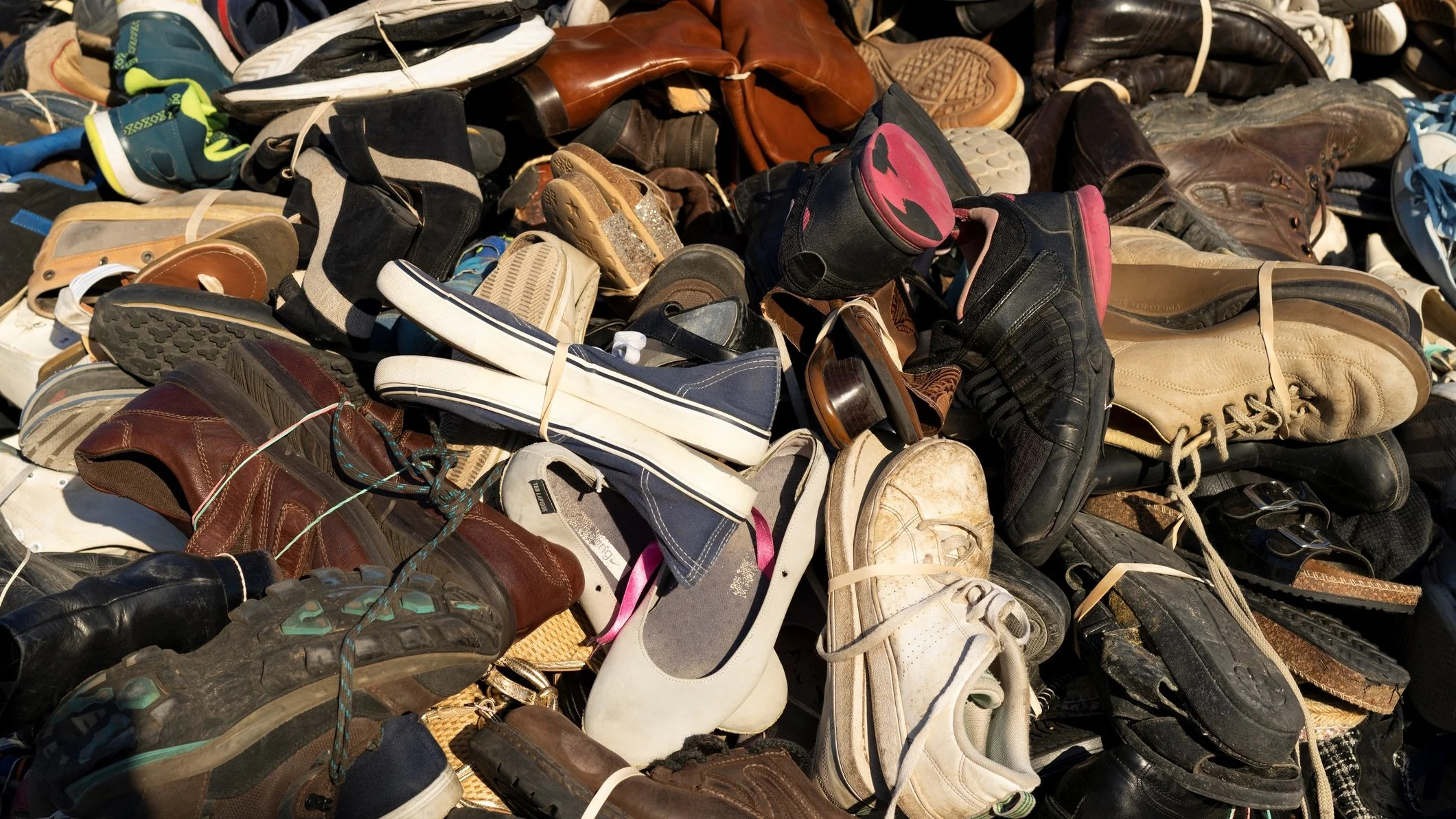
Waste management includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its disposal. Footwear contributes approx. 17% of solid waste in Indian landfills.
Footwear Industry
•In India, industries were formed after the invasions of the Dutch, Portuguese, and British. In 1887, India saw the foundation of its first shoe factory.
•The brand 'BATA' was founded in 1894, and it upscaled the booming footwear market.
•India is presently the world's second largest manufacturer and consumer of footwear, accounting for 10.7% of worldwide output.
•In India, the footwear industry is a significant segment of the leather industry.
Secondary Research
Qualitative and Quantitative research
Field visits with stakeholders
Project Goals
•Look into the Indian footwear industry's waste management techniques.
•The end-of-life shoe regional disposal methods, as well as the causes and effects of waste management, are dictated by the nature of the topic.
•The scope of this study is to evaluate the entire journey of waste generated by end-of-life shoes in the Indian footwear industry.
Data Mapping
Redefining the Design Brief
Waste Management of the Footwear Industry In India of PU & Leather
Waste Management of the Leather Footwear Industry In India
Why We Choose Leather?
•It produces large amounts of waste during the manufacturing process and after the use of leather fabric by consumers making it one of the largest waste-producing industries.
• Leather also contributes to 60% of the overall footwear waste and 10% of the municipal waste
•India carries 13% of the world’s leather production
•Leather shoes can take around 20-40 years to decompose
•In the past we have seen that leather has the potential to be sustainable
Why Leather and not PU?
•The process of regeneration & re-purposing of PU is a complex and wasteful
•PU is biodegradable and naturally degrades a lot quicker than leather
•Leather can be regenerated & reused multiple times
•When compared to leather cutting and trimming techniques, PU is manufactured by molding which is less wasteful
Insights on PU from our field visit :
As part of our research, we visited the PU manufacturing and assembly industries to gain a better understanding of the process of making PU Shoes before picking which material to work on
Footwear waste is one of the most contaminating marine pollutants, as a result of the product's withering, most parts disintegrate into incomprehensible, degraded fragmented parts, such as the base of slippers, straps, shoe laces, and so forth. An inefficient solid waste system can have adverse effects on the environment such as contamination of land and water, the spread of infectious illnesses, the clogging of drains, and the loss of biodiversity.
Initial Design Brief
Field Site
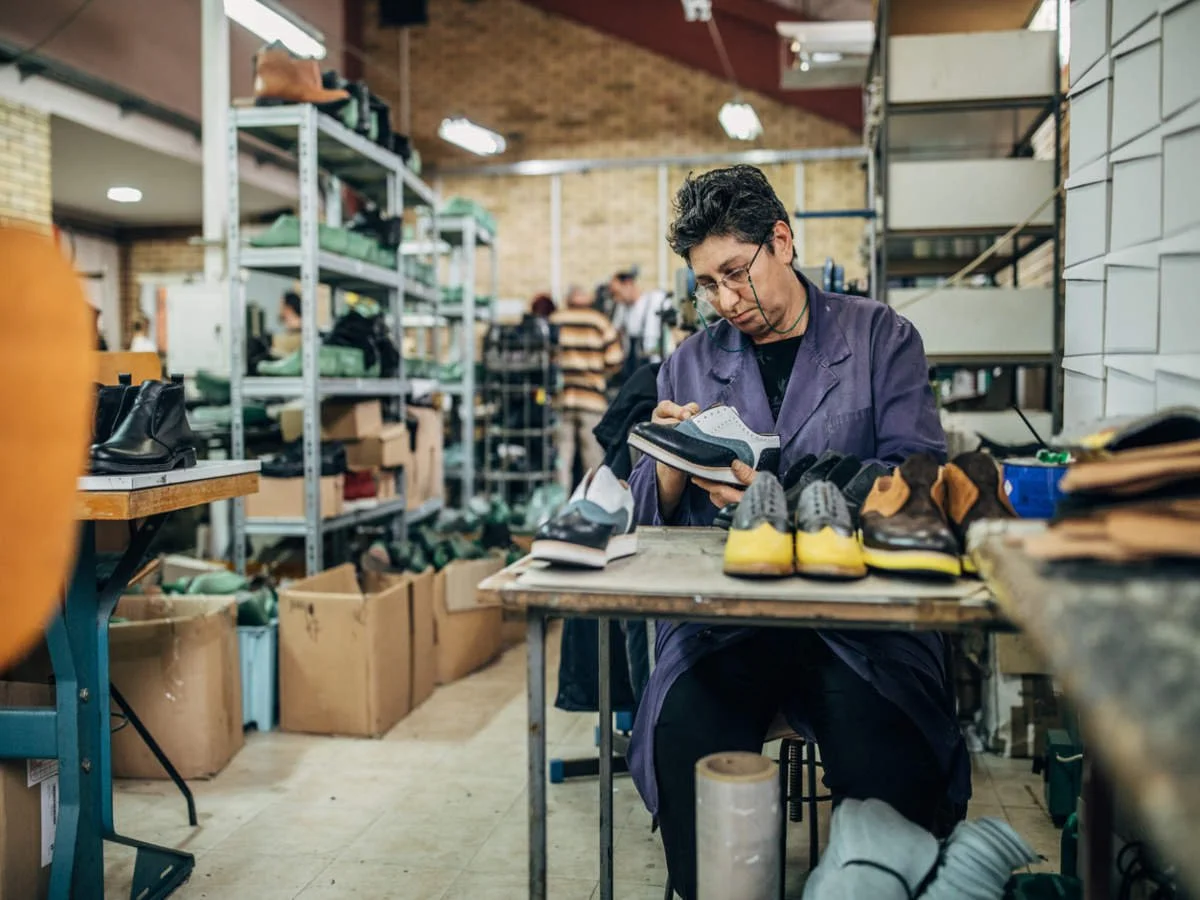
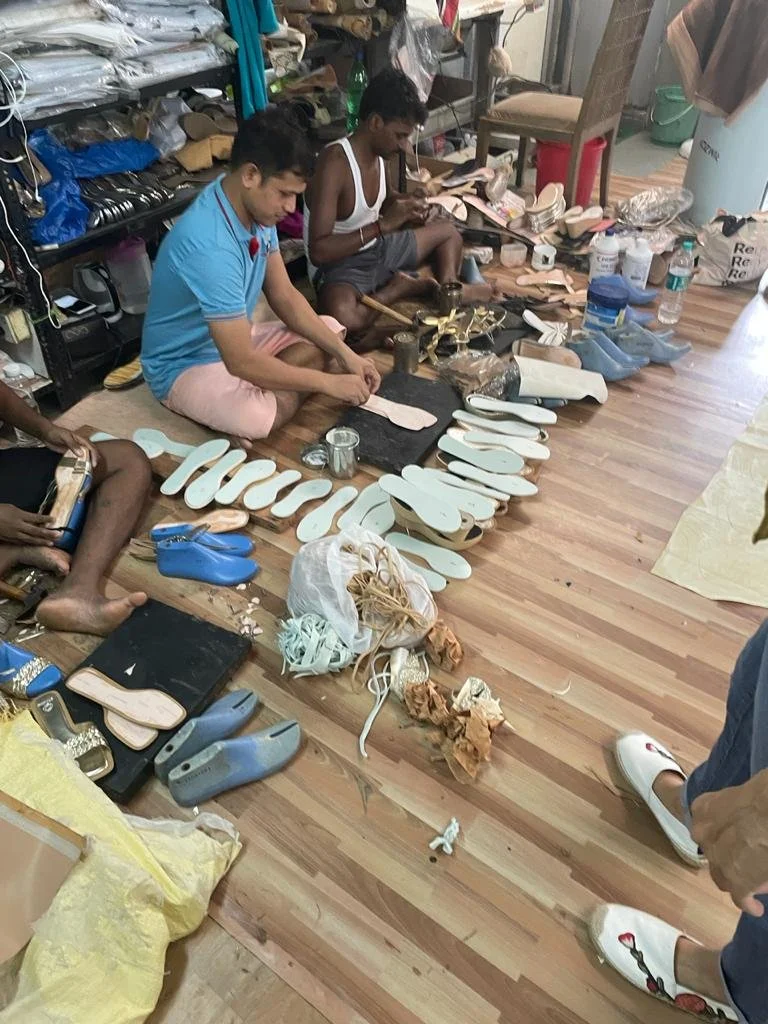
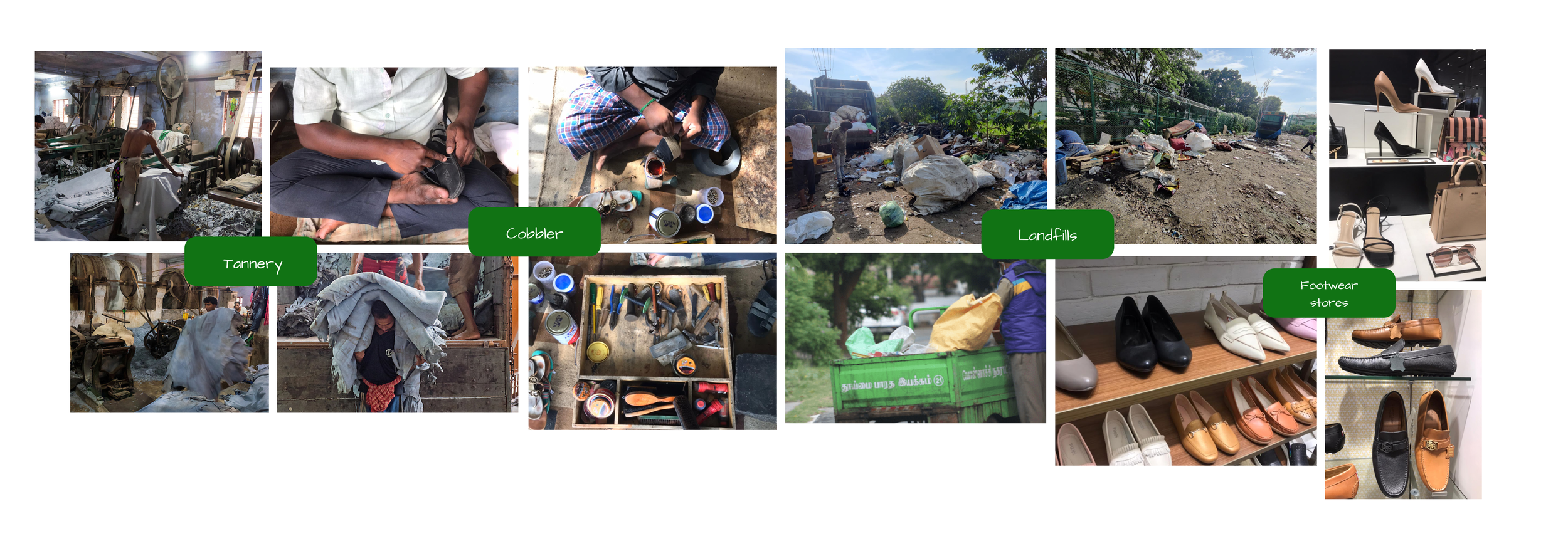
In order to understand the manufacturing of leather shoes and the stakeholders involved we carried out a field visit in which interviews were taken to understand the core problem. There we looked into 4 aspects of leather production - tanneries(manufacturing), cobblers (fix and assembly), leather shoe stores, and rag pickers from dump yards to betters understand the behavioral aspects of various users.
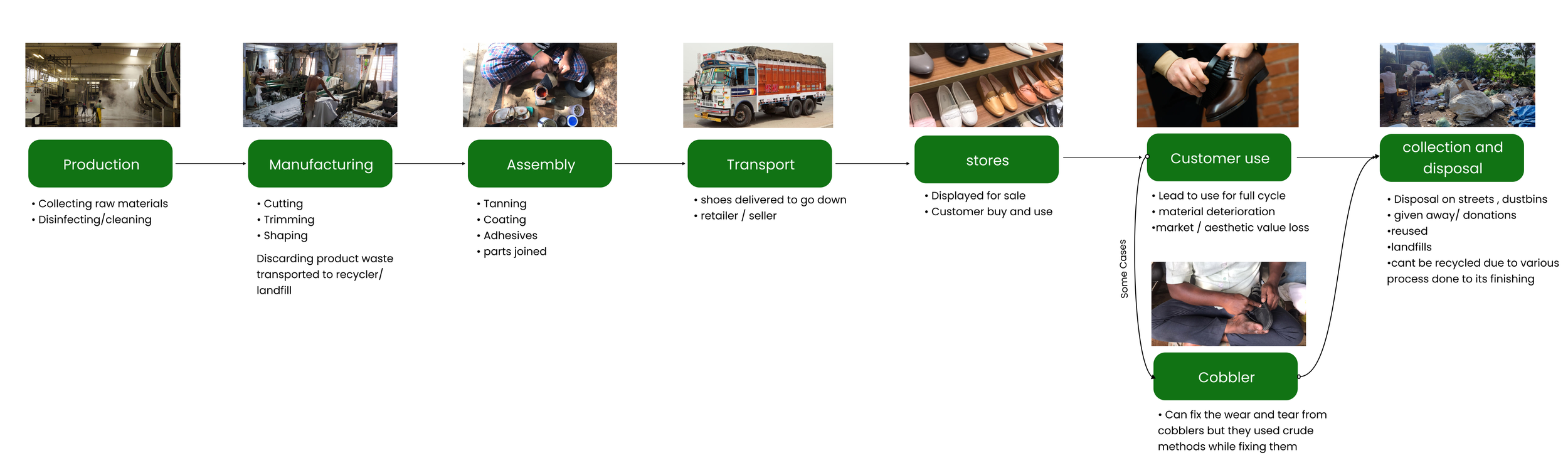
User Journey Map
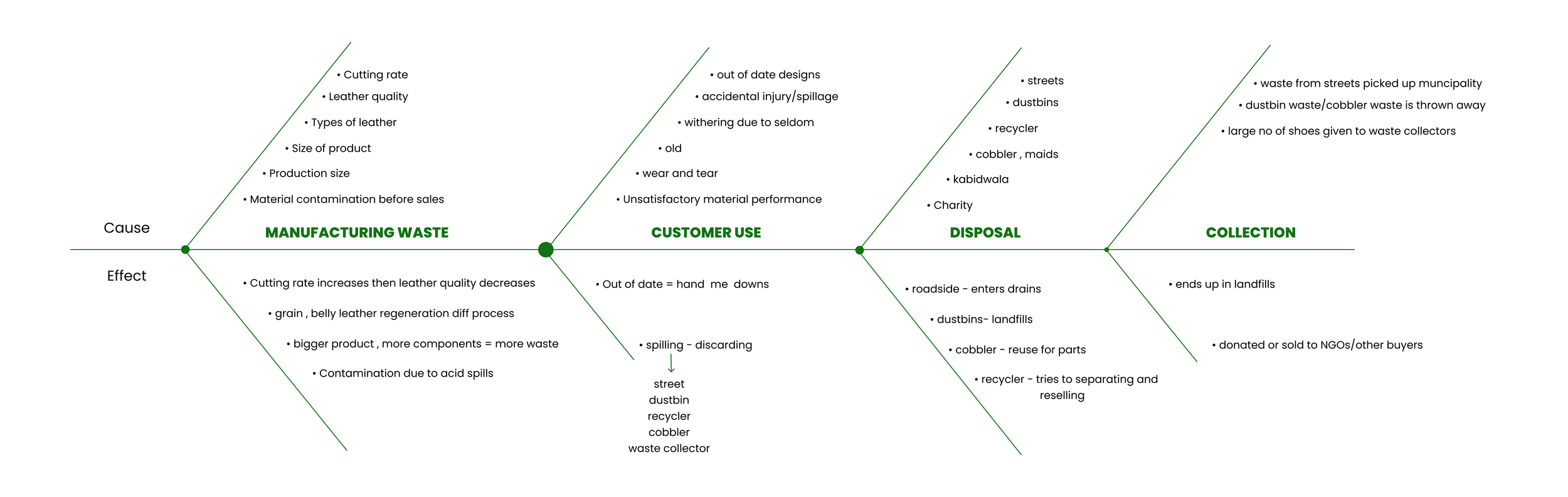
Fish Bone Diagram
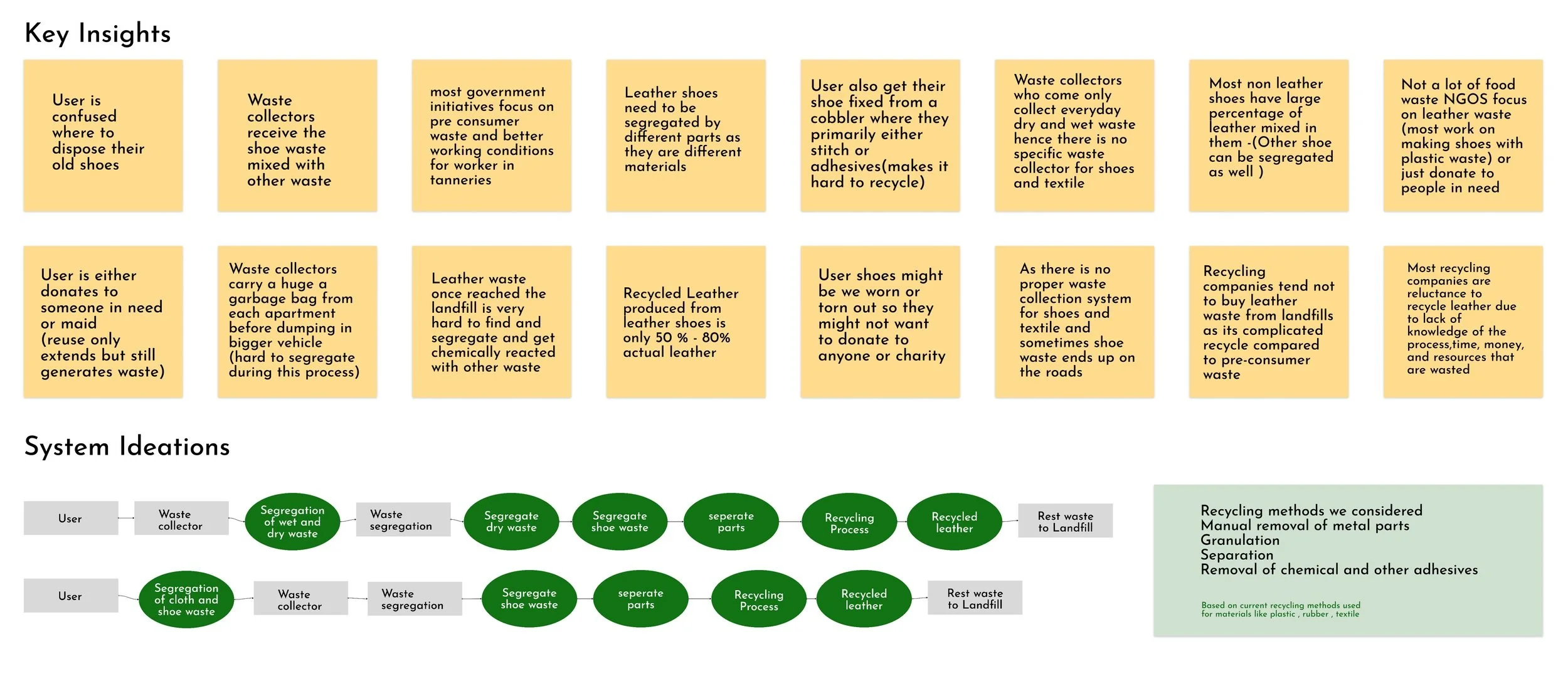
From our conclusion regarding the type of waste produced during the making of leather shoes, we were able to make a fishbone diagram to help us identify possible causes of the waste produced and in sorting ideas into these categories by looking into the cause and effect.
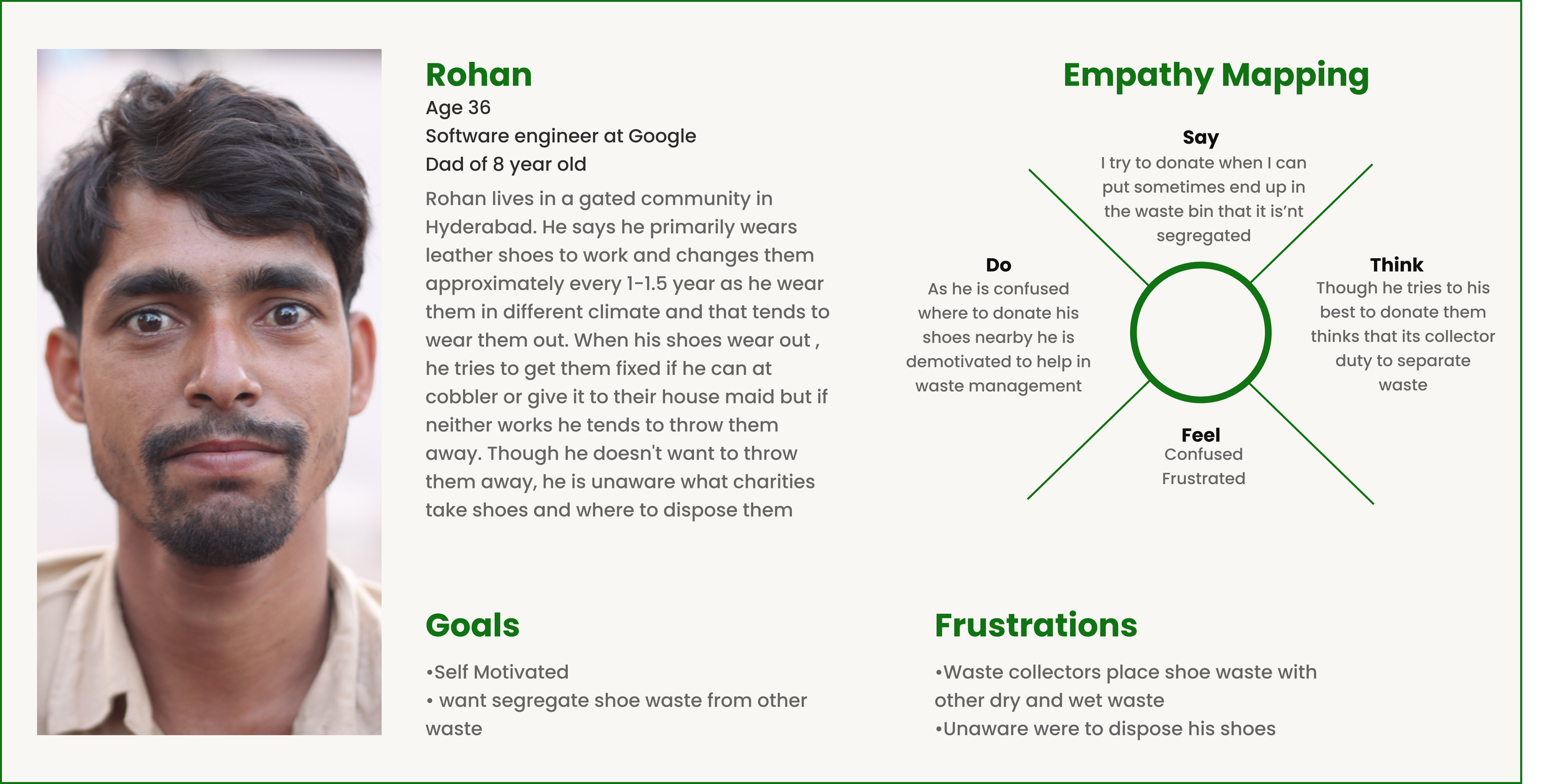
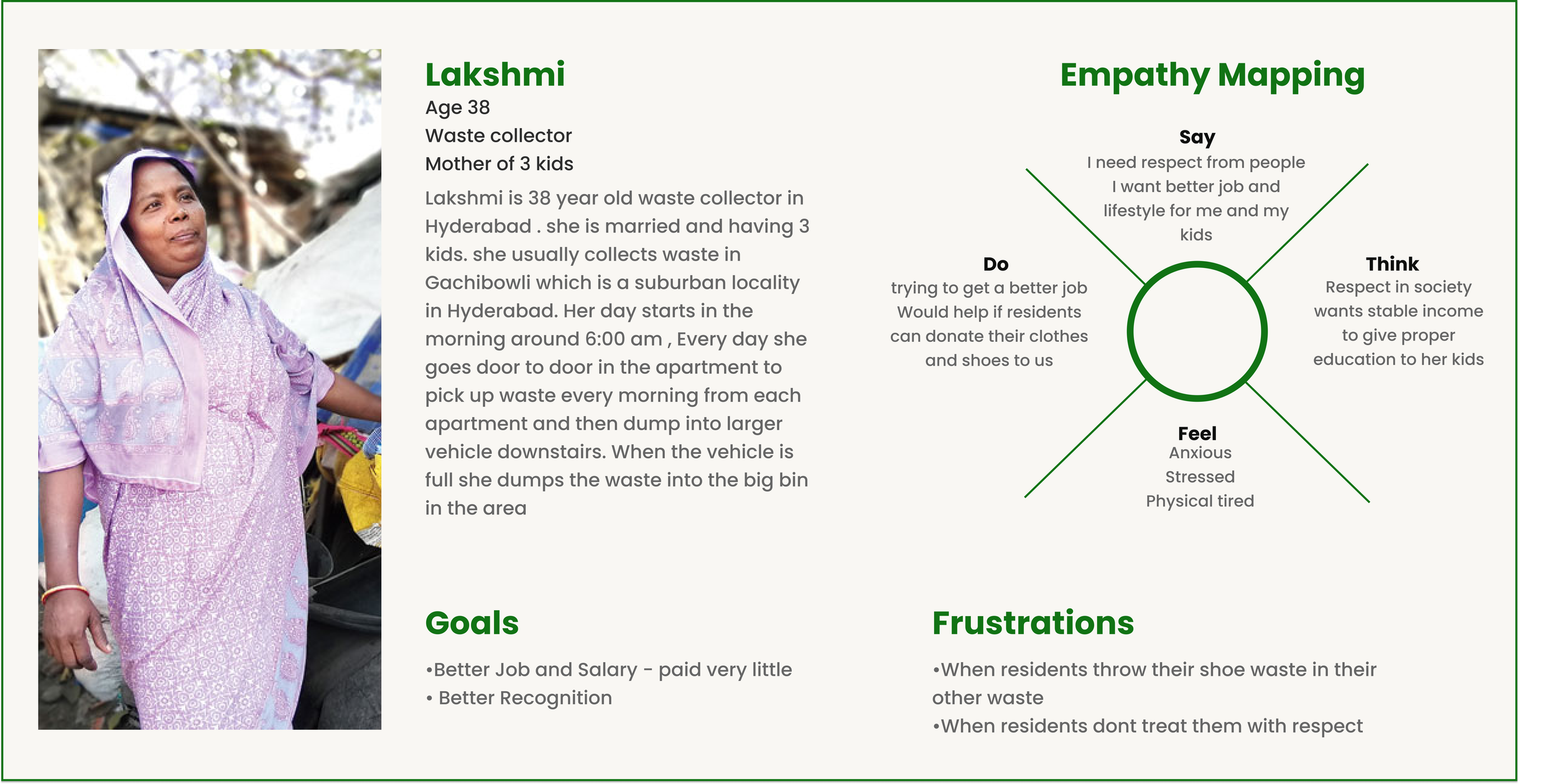
Based on our discussions with the stakeholders and insights from our affinity mapping from the field visit, we were able to determine the user journey of leather shoes
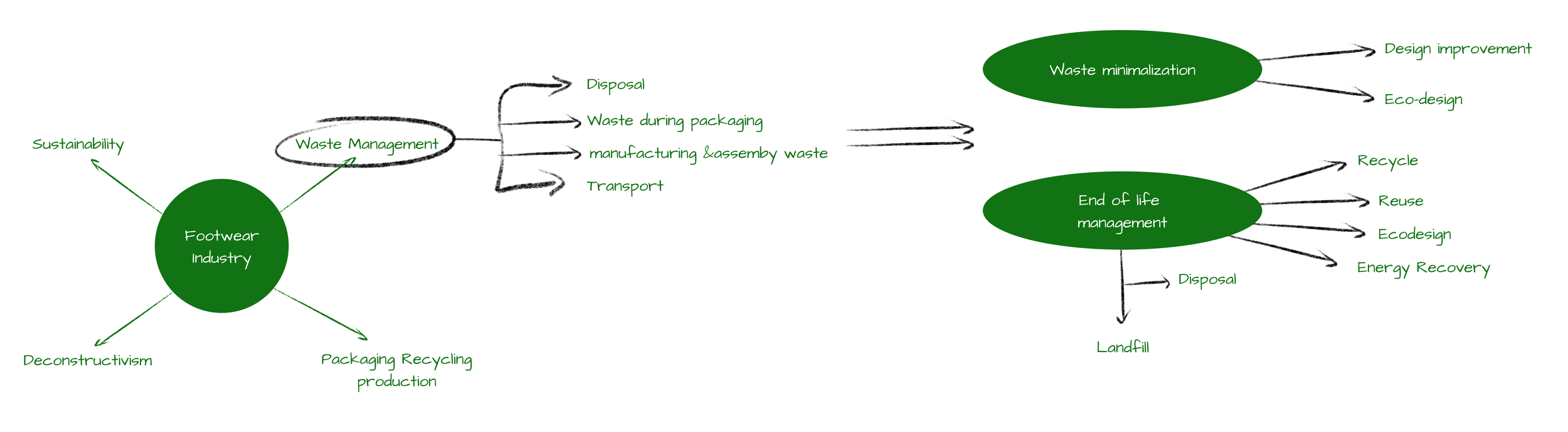
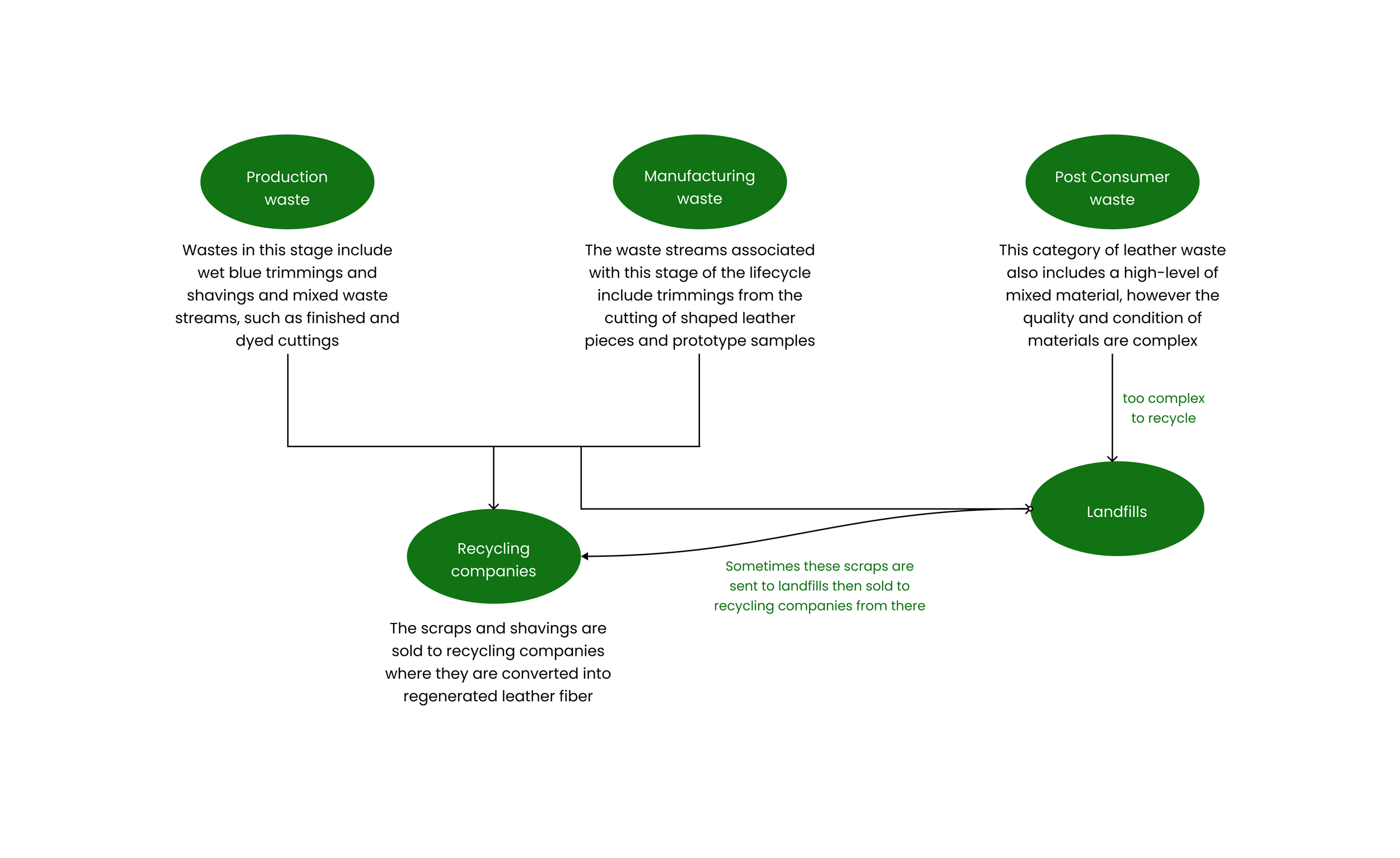
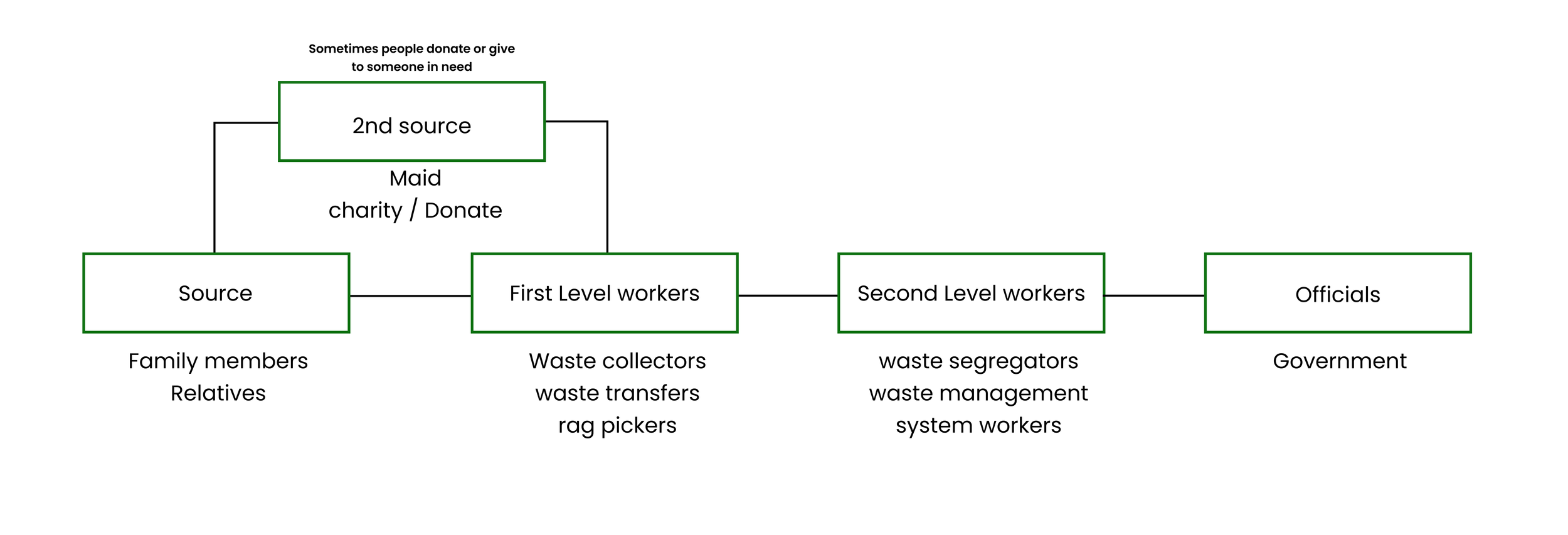
Based on our insights from the user journey and interviews from our stakeholders, we were able to conclude that there are two types of waste produced in the making of leather shoes - Post-consumer waste and Pre-consumer waste ( Production and Manufacturing)
The Steps taken currently to manage waste in Leather Industry
Reduce: You can reduce the amount you buy leather goods or look into sustainable alternatives like cacti, pineapple leaves, and mycelium which are reducing the environmental impact of leather production.
Reuse: You can donate your worn leather shoes to a local charity or house help. Many non-profit organizations will collect used footwear and you can pass it on to those in need in the community.
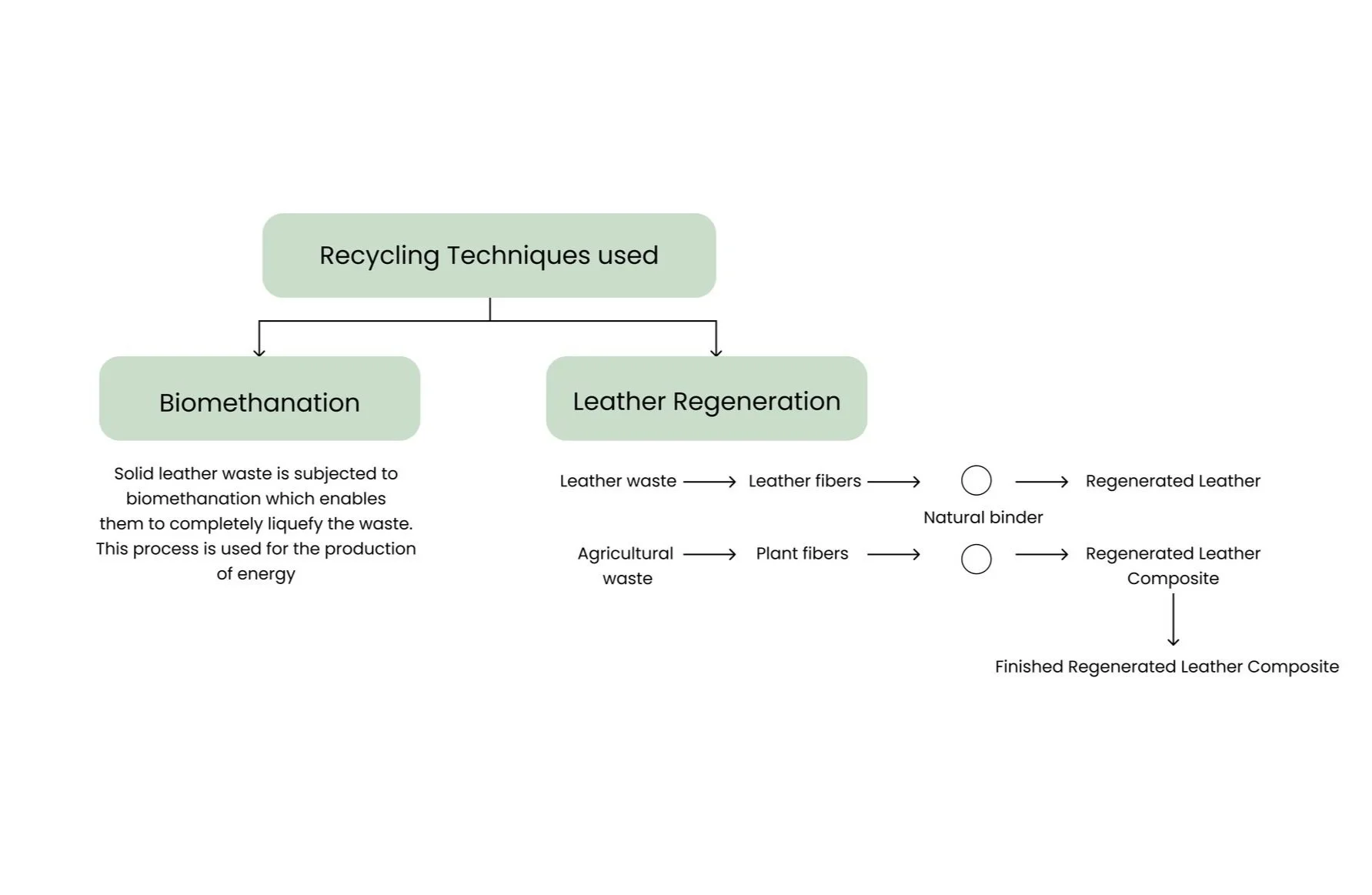
Recycling: Most of the discarded leather waste in the pre-consumer stage is untreated and not mixed with other materials so typically they are bought by companies that recycle leather where they find a way to recycle most of the scraps and shavings to form regenerated leather before it goes into the landfill by the methods shown below
Focus Points
Affinity Mapping
Stakeholders in these Focus Points
Existing System
Consumer Behavior On Leather waste
Stakeholder personas
Government Initiatives
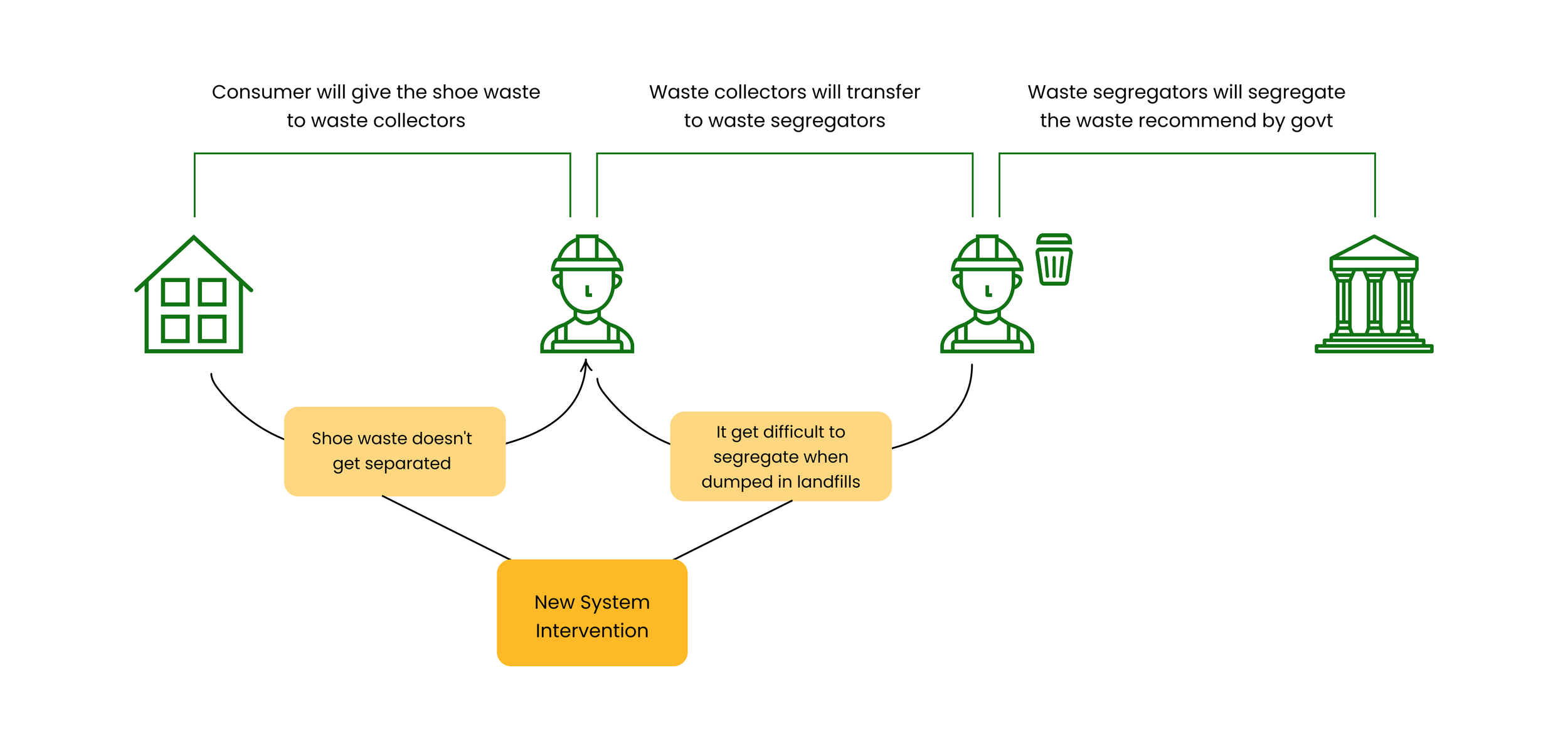
Opportunity System Intervention
How Might We improve waste management for the Indian leather shoe industry by incorporating better methods of segregation and recycling for the post-consumer waste created?
Problem Statement
Mind Mapping and Insights
Final System